The number of people diagnosed in the UK with coeliac disease has increased fourfold between 1990 and 2011, a study suggests, with an estimated one in 100 people in the UK suffering from the disease. With more and more people being diagnosed in recent years, awareness of coeliac disease has never been so widespread. But here’s 15 facts about coeliac disease you probably didn’t know…
1. Coeliac disease is an auto immune disease

Coeliac disease is an immune disease, much like type 1 diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, and multiple sclerosis, in which people can’t eat gluten because it will damage their small intestine. Gluten is a protein found in wheat, rye, malt and barley. Gluten can also be found in oats, however whilst oats do not contain gluten, they do contain the protein avenin to which only about 5% of coeliacs are intolerant. Gluten may also be used in products such as vitamin and nutrient supplements, lip balms, and some medicines.
2. There are over 300 known symptoms of coeliac disease
Coeliac disease can be difficult to diagnose because it affects people differently. In fact, some people with coeliac disease have no symptoms at all. Coeliac disease symptoms also include: unexplained iron deficiency anaemia, fatigue, bone or joint pain, seizures or migraines, depression, osteoporosis, and an itchy skin rash called dermatitis herpetiformis.
3. 1 in 100 people worldwide suffer from coeliac disease
That’s more than Crohn’s, colitis and cystic fibrosis combined, and about one in 100 children has coeliac disease, making it one of the most common conditions in children. It is estimated that more than 90% of those affected by coeliac disease are not aware that they have it.
4. Coeliac disease is hereditary.

People with a first-degree relative suffering with coeliac disease (parent, child, sibling) have a 1 in 10 risk of developing coeliac disease. First-degree relatives should be retested every 3 – 4 yrs as coeliac disease can present at any time throughout one’s life.
5. About 20 to 25% with coeliac disease break out in an intensely itchy & painful rash known as dermatitis herpetiformis.

6. Left untreated, coeliac disease can lead to additional serious health problems
In untreated coeliac disease, the villi (the area which is responsible for absorbing nutrients in your small intestine) can become inflamed and flattened, or even disappear. That’s why it’s really important to stick to your gluten-free diet as treatment for the condition. Additionally, coeliac suffers may also develop other autoimmune disorders, such as type I diabetes, multiple sclerosis (MS), osteoporosis, and gastrointestinal cancers, and also conditions such as anemia, osteoporosis, infertility and miscarriage, neurological conditions like epilepsy and migraines, short stature, and intestinal cancers.
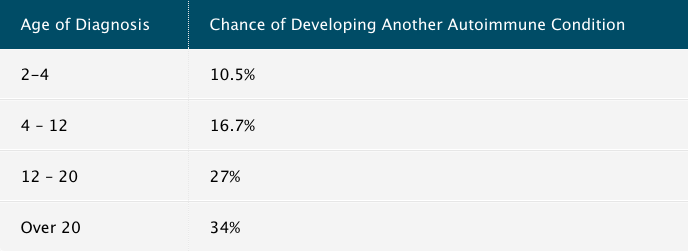
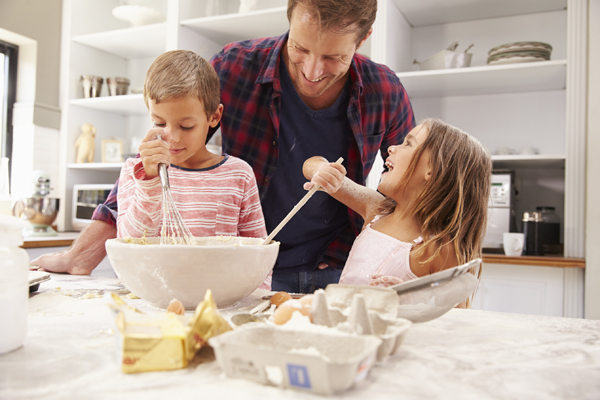
7. The later the age of diagnosis, the greater the chance of developing another autoimmune disorder
If you think you might have coeliac disease, it’s best to get tested as soon as possible! In a 1999 study, Ventura, et al. found that for people with coeliac disease, the later the age of diagnosis, the greater the chance of developing another autoimmune disorder. It’s especially important to get tested if you have family members with coeliac disease as it is hereditary.
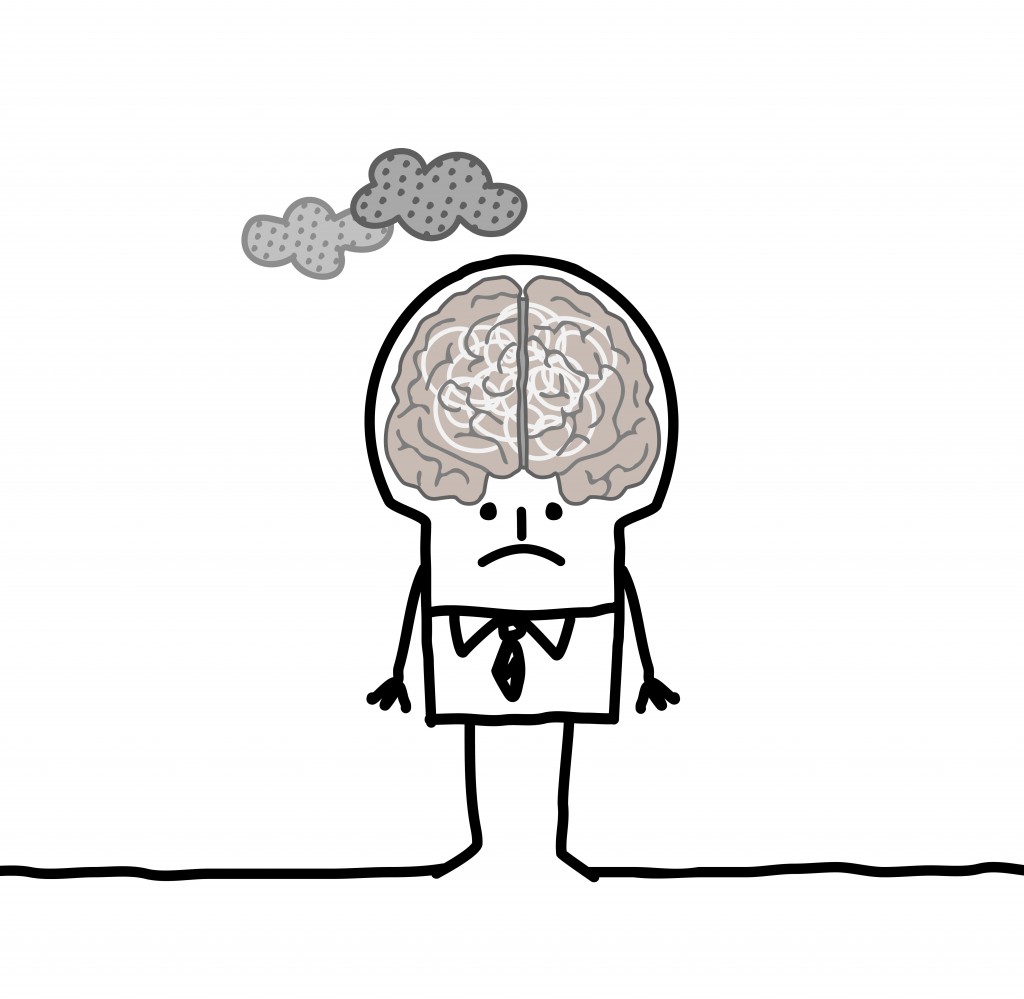
8. Many people with coeliac disease report having “Brain Fog”
Many people with coeliac disease report having “brain fog”, a form of cognitive impairment that can encompass disorientation, problems with staying focused and paying attention, and lapses in short-term memory.
9. Currently, the only treatment for coeliac disease is lifelong adherence to a strict gluten-free diet.

People living gluten-free must avoid foods with wheat, rye and barley, such as bread and beer. Ingesting small amounts of gluten, like crumbs from a cutting board or toaster, can trigger small intestine damage.
10. It’s not just food that can cause coeliacs to be ‘glutened’.
There are many unexpected products which contain wheat, such as beauty products like tooth paste, that can cause symptoms to flare up in coeliacs. Some other unexpected ways you can be ‘accidentally glutened‘ is by kissing people who have recently eaten gluten, young children playing with Play-Doh (which contains wheat flour) often ingest this product, and by touching pet foods containing gluten.
11. Gluten May Cause Depression in People with Non-Coeliac Gluten Sensitivity

A study published in 2014 theorised that the reason some people “feel better” on a gluten- free diet is that gluten has a negative effect on their mental state, although exactly how gluten causes a change in mental state is still unknown. Scientists have suggested that gluten might affect the amount of serotonin produced in the brain, which serves as a neurotransmitter in the brain most commonly thought of as how the way our brain gives us feelings of happiness.
12. Coeliac disease is also known as coeliac disease, coeliac sprue, non-tropical sprue, and gluten sensitive enteropathy.

13. Coeliac disease declined during the bread shortages of the Second World War but climbed again after the war when these products became more readily available again.

14. You can test negative for coeliac and still have the disease when it is “triggered” later on in life.
It’s possible to have a negative blood test and still have coeliac disease. If you weren’t eating gluten at the time of your blood test, or you had limited your gluten intake, you may have received an inaccurate result. However, once coeliac is triggered, it is a life-long disease.
15. Even very small amounts of gluten can be damaging to people with coeliac disease. Therefore, taking sensible steps to avoid cross contamination with gluten is important.
Top tips include:
- keep cooking utensils separate during food preparation and cooking
- avoid frying food in the same oil that has previously been used to cook foods which contain gluten
- use a clean grill, separate toaster or toaster bags to make gluten-free toast
- use separate breadboards and wash surfaces thoroughly
- use separate condiments like jam, butter, mustard and mayonnaise.